Feature Overview
-
Package Management: Browse, search, install, and uninstall Ruyi packages from the VS Code sidebar.
-
Virtual Environments: Create and activate Ruyi venvs with a wizard; terminals and build tools automatically inherit the environment.
-
News & Status Bar: Access news from the status bar, view indicators, and switch the current virtual environment.
-
Source Package Extraction: Right‑click in the Explorer to quickly download and unpack official examples or source packages.
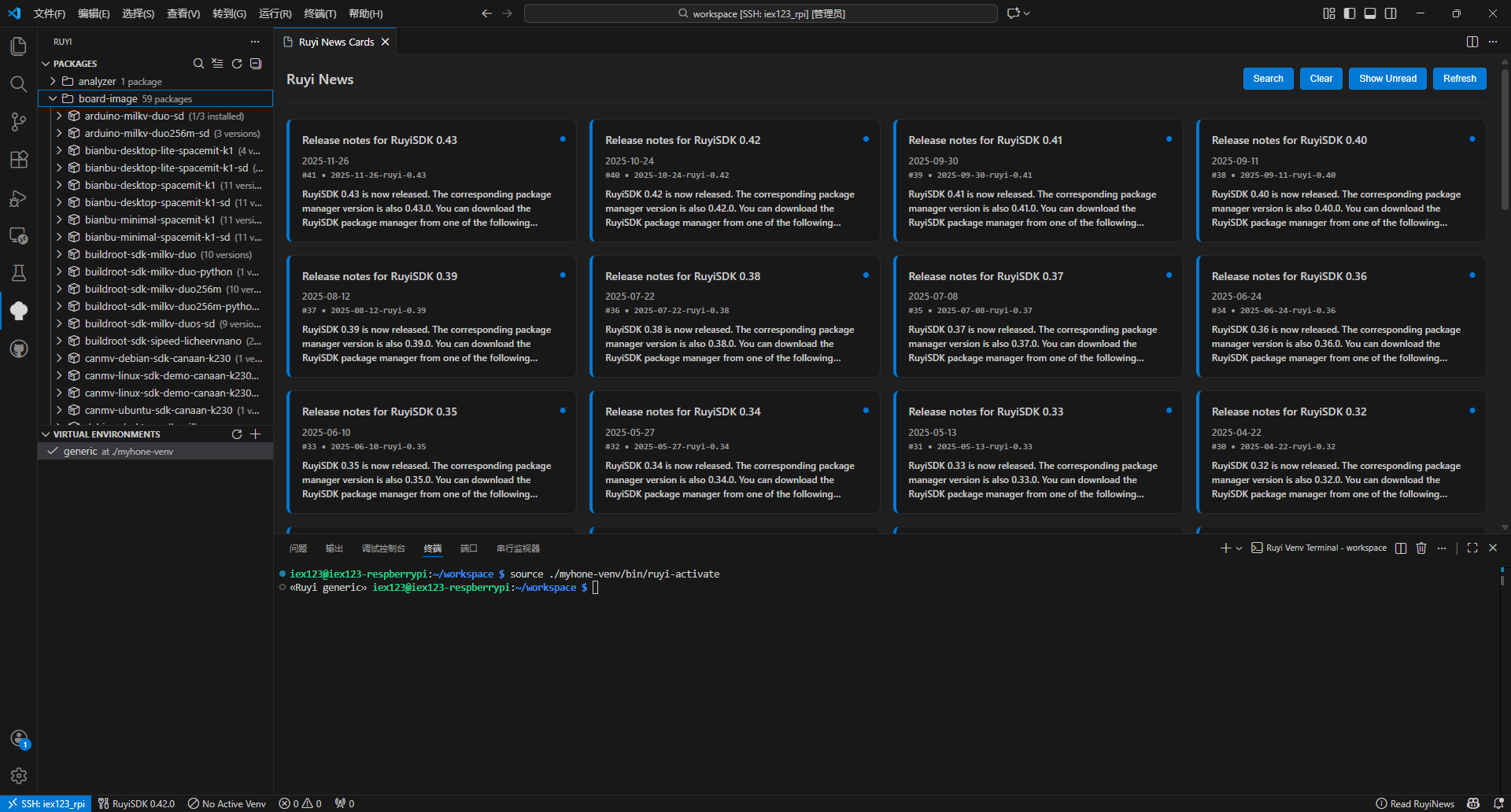
For detailed instructions, please refer to the respective subpages under “User Guide”(Packages、Virtual Environments、News、Extract RuyiSDK Package).
Interface Highlights
- Entry Point: The Ruyi icon in the sidebar Activity Bar provides access to the Packages and Virtual Environments views; the bottom status bar displays the current virtual environment and the news entry.
- Virtual Environments: Click a virtual environment in the list to activate it. The integrated terminal and CMake/Meson builds will then inherit the PATH and cross‑compilation settings (from files such as toolchain.cmake and meson-cross.ini in the venv directory).
Development Workflow Example
The following example demonstrates how to use the extension in VS Code to complete a minimal RISC-V cross‑compilation and execution process, making it easy to get started quickly.
Hello World: Minimal Cross‑Compilation and Execution with Extension
- In the Packages view, install the
gnu-upstreamtoolchain (optionally installqemu-user-riscv-upstreamfor local simulation). - In the Virtual Environments view, click
+, select thegenericProfile, choose thegnu-upstreamtoolchain, specify a name and path, then create and activate the virtual environment. - In the workspace, create a new file
hello.cwith the following content:
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
printf("Hello, RuyiSDK!\n");
return 0;
}
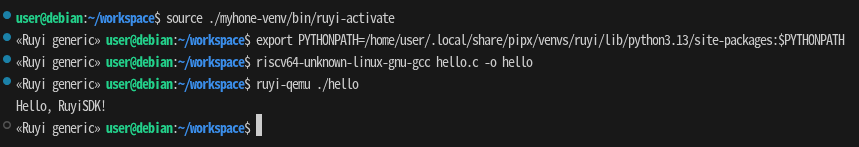
- Open the VS Code terminal (with the venv activated) and execute the build and run:
riscv64-unknown-linux-gnu-gcc hello.c -o hello
ruyi-qemu ./hello
Currently, installing Ruyi via pipx has known issues(see https://github.com/ruyisdk/ruyisdk/issues/414). If you are using the extension installed with pipx, you must first run
pipx ensurepathand restart the terminal to ensureruyi-qemuis available. In addition, set thePYTHONPATHenvironment variable to point to the pipx Ruyi installation path, for example:export PYTHONPATH="$HOME/.local/pipx/venvs/ruyi/lib/python3.x/site-packages:$PYTHONPATH"
If the output is Hello, RuyiSDK!, the build and run were successful.
Notes
- If not using QEMU, you can deploy the executable to the target device for execution. Refer to the official documentation or relevant case studies for deployment methods.
- For more complex builds (such as CoreMark), please refer to CoreMark (Example: LicheePi 4A).
More Information
- Extension repository and issue tracker: https://github.com/ruyisdk/ruyisdk-vscode-extension
- RuyiSDK official site: https://ruyisdk.org/